Investment Analysis of Superconducting Quantum Computers
2025.11.26 · Blog quantum investment analysis
Why Superconducting Quantum Computers Are a High-Value Investment Frontier
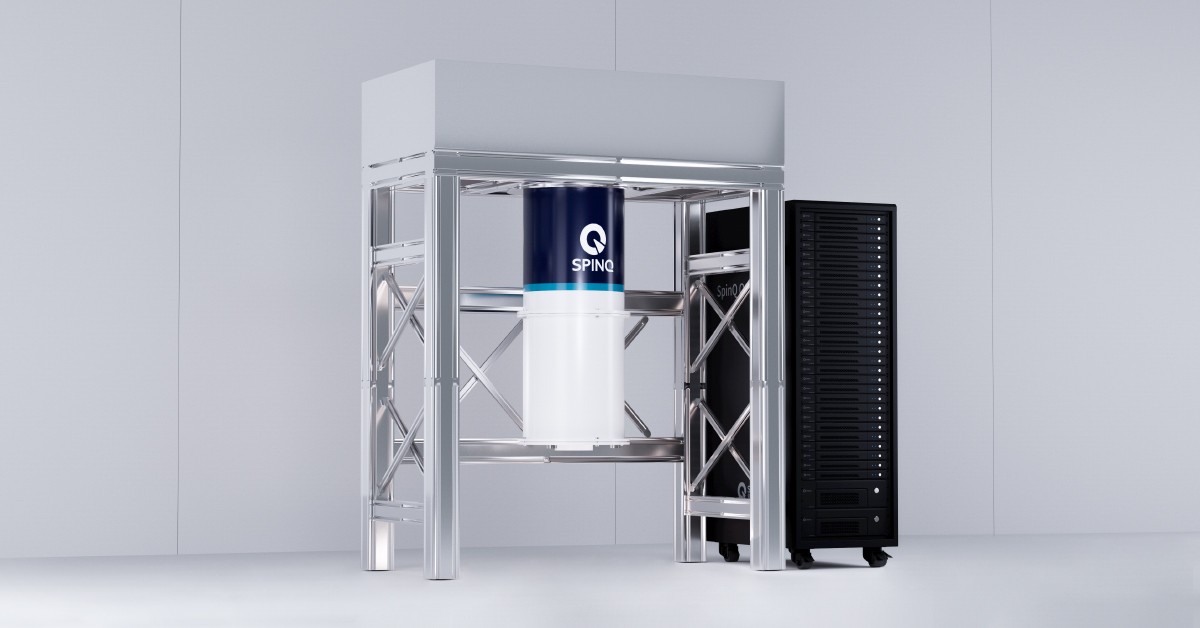

Superconducting quantum computers have moved from theoretical potential to practical engineering reality. Over the last decade, this technology has become the leading platform for near-term quantum computation, driven by the rapid advancement of high-fidelity qubits, scalable chip designs, and increasingly mature cryogenic and control infrastructures. For investors, superconducting quantum computers represent one of the most compelling deep-tech opportunities of the next decade—an industry with long-term defensibility, strategic national value, and large-scale commercial application potential.
Several factors explain why investment interest is accelerating. First, superconducting chips have demonstrated consistent improvements in coherence time, gate fidelity, and coupling control, allowing more stable computation compared to many competing technologies. Second, market demand from AI, biopharma, finance, and advanced research is rising. Organizations in these fields are under pressure to handle larger datasets, simulate complex systems, and speed up algorithmic optimization—areas where quantum computing offers significant upside. As superconducting technology continues to mature, investors increasingly view it as a foundational layer of future high-performance computing infrastructure.
The next sections break down the technology landscape, the market forces shaping investment value, and the strategic advantages of key players such as SpinQ.
How Superconducting Quantum Computers Work and Why They Lead the Market
Fundamental Architecture and Advantages of Superconducting Qubits
Superconducting quantum computers rely on circuits made from materials that reach a superconducting state at millikelvin temperatures. These circuits, often containing Josephson junctions, behave like artificial atoms that can encode qubits. Because this architecture uses well-established semiconductor fabrication techniques, it offers an industrial advantage: qubit arrays can scale through lithography, deposition techniques, and advanced chip packaging.
The primary advantages include:
-
Scalability: Superconducting qubits are easier to manufacture at scale compared to ion traps or photonic systems.
-
High gate speed: Superconducting qubits operate in the nanosecond regime, enabling fast circuit execution.
-
Strong coupling control: Engineers can achieve precise qubit interactions and tunable couplings.
-
Compatibility with existing chipmaking ecosystems: This provides a pathway for multi-qubit processors and eventual large-scale quantum architectures.
These factors make superconducting quantum computers one of the most commercially mature technologies available today.
Performance Factors That Drive Investment Value
Investors often evaluate superconducting quantum computing through three performance metrics:
-
Coherence Time: Determines how long qubits retain quantum information.
-
Gate Fidelity: A measure of how accurately a quantum operation executes.
-
Readout Precision: Determines the reliability of extracting computation results.
Modern superconducting chips exhibit significant improvements on all three metrics, largely due to enhanced chip design, improved material quality, and advanced cryogenic engineering.
The Role of Integrated Hardware Ecosystems
The superconducting quantum computer is more than just the chip—it requires an entire orchestration of advanced components:
-
Ultra-low-temperature cryogenic systems
-
High-precision measurement and control hardware
-
FPGA-based signal processing
-
Calibration and benchmarking software
Companies such as SpinQ integrate these components into cohesive systems. For example, SpinQ's superconducting offerings include high-Q chip architectures, modular measurement and control systems, and complete deployment services for low-temperature laboratory environments. This integrated approach lowers barriers to adoption and increases the commercial value of the platform.
Market Landscape — Growth Drivers, Industry Forces, and Competitive Positioning
Key Industrial Growth Drivers
Demand for superconducting quantum computers is accelerating across multiple industries:
-
Artificial Intelligence: Quantum algorithms for optimization and sampling support next-generation AI model development.
-
Biopharma: Quantum simulation accelerates molecular modeling and drug discovery workflows.
-
Financial Services: Institutions explore quantum tools for risk modeling, option pricing, and portfolio optimization.
-
Scientific Research: Universities and laboratories deploy real quantum hardware for algorithm, materials science, and physics research.
-
Education: Institutions are adopting real quantum machines to train the next generation of quantum engineers.
These use cases create a strong foundation for long-term recurring investment growth.
Application Sectors Likely to Produce Near-Term Returns
-
Cloud-based quantum computation
-
Quantum education and training systems
-
Specialized algorithms for finance and molecular modeling
-
Turnkey superconducting labs for universities and research centers
These markets generate practical, near-term revenue even before fully fault-tolerant quantum computing becomes available.
Investment Evaluation — Capabilities, Product Strengths, and Business Advantage of SpinQ
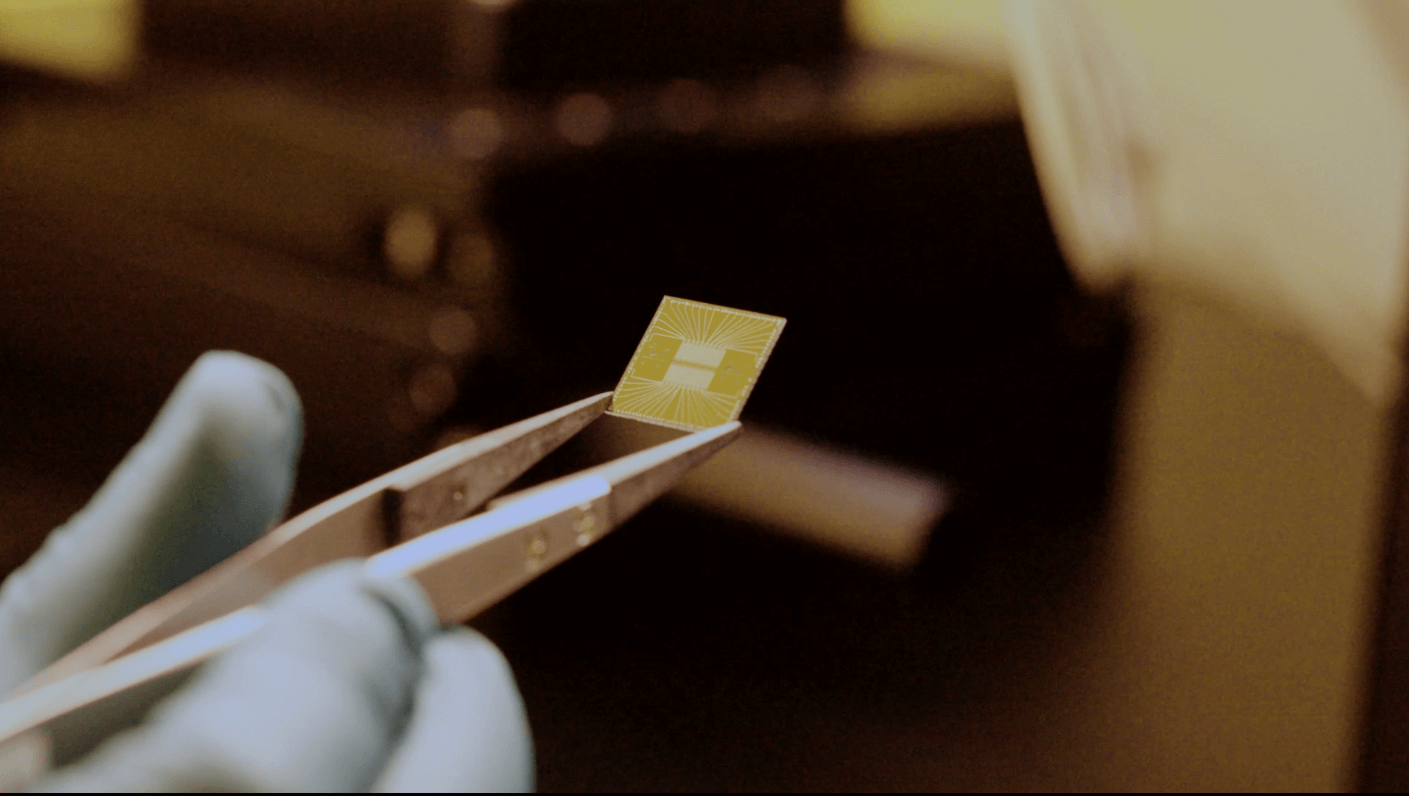
SpinQ provides one of the most comprehensive quantum product ecosystems available today. For investors, the company represents a rare combination of hardware innovation, commercial deployment experience, and industrial software capability.
Commercial Superconducting Hardware: "SPINQ QPU C Series" Chips and "SPINQ SQC"Systems
SpinQ's superconducting portfolio includes:
-
"SPINQ QPU C Series" superconducting quantum chips:
-
Engineered for high stability in millikelvin environments.
-
Demonstrate high Qi values, long qubit lifetimes, and strong reliability.
-
Designed with scalability in mind, supporting growing qubit counts.
-
-
"SPINQ SQC"superconducting quantum computer:
-
Built on advanced Josephson-junction circuits.
-
Offers strong coherence, high-fidelity gates, and precise multi-qubit control.
-
Positioned as an industrial-grade machine supporting research and commercial applications.
-
This hardware foundation aligns with major investment trends centered on scalable superconducting architectures.
Full-Stack Ecosystem Strength
SpinQ stands out because it offers more than hardware. Its ecosystem includes:
-
SPINQ Cloud — Multi-qubit real devices and high-performance simulation environments.
-
SPINQ QEDA — An automated EDA tool enabling rapid circuit layout, parameter tuning, and routing optimization.
-
SpinQit — A Python-based development environment supporting algorithm execution on hardware, simulators, and cloud systems.
This software stack creates additional recurring revenue pathways and lowers customer onboarding costs.
Revenue Pathways and Customer Segments
SpinQ sells to multiple high-value B2B markets:
-
Education: Universities seeking hands-on quantum systems.
-
Research institutions: Laboratories requiring superconducting or NMR-based experimentation.
-
Financial institutions: Quantum-assisted optimization exploration.
-
Biopharmaceutical companies: Molecular simulation and drug discovery acceleration.
-
AI companies: Quantum-enhanced model optimization.
These diverse segments expand revenue stability and reduce dependence on any single market.
Competitive Advantages Strengthening Investment Appeal
-
First Chinese company exporting superconducting quantum chips internationally
-
Creator of the world’s first programmable desktop quantum computer
-
A multidisciplinary team from globally recognized research universities
-
Solutions spanning education, research, AI, finance, and biopharma
This combination creates a balanced, resilient long-term investment opportunity.
Risk Assessment — Challenges, Cost Structures, and Market Uncertainties
Technical Barriers and Scalability Risks
Superconducting technology faces several engineering challenges:
-
Achieving larger qubit arrays while maintaining coherence
-
Managing cross-talk and frequency collisions
-
Ensuring precise control across increasingly complex qubit networks
-
Expanding cryogenic infrastructure for larger systems
These factors require ongoing R&D and long-term capital investment.
Market Adoption Challenges
Quantum computing is still in early commercial stages. While demand is rising, some customers remain cautious:
-
Enterprises need clearer ROI models.
-
Industry-specific algorithms need more testing.
-
Cloud-based quantum access competes with on-premise hardware deployment decisions.
Overcoming these challenges requires strong application development ecosystems, customer education, and early demonstration wins.
Supply Chain and Infrastructure Limitations
Superconducting quantum computers rely on:
-
Dilution refrigerators
-
High-end microwave electronics
-
Specialized chip fabrication capacity
-
Highly trained quantum engineers
These supply chain components can become bottlenecks as global demand increases.
Strategic Investment Recommendations — Timelines, Scenarios, and Portfolio Positioning
Short-Term Opportunities (2025–2026)
High-return, low-risk areas:
-
Quantum cloud services
-
Education-focused quantum hardware
-
NMR-based teaching systems
-
Entry-level algorithm development projects
-
Small-scale superconducting systems for research labs
These sectors already generate revenue and have proven adoption curves.
Mid-Term Opportunities (2026–2028)
Growing opportunities:
-
Quantum chip design automation
-
Measurement and control systems
-
Cryogenic lab deployment services
-
Domain-specific quantum algorithms for finance and AI
These markets scale as quantum computing becomes more integrated into enterprise R&D workflows.
Long-Term Value (2028–2030+)
High-risk, high-reward potential:
-
Large multi-qubit superconducting quantum processors
-
Hybrid quantum–classical AI pipelines
-
Full-stack quantum computing infrastructure for national-scale research centers
These areas align with global trends toward quantum acceleration and high-performance computing integration.
The Investment Outlook for Superconducting Quantum Computers
Superconducting quantum computers stand at the center of the next wave of computational innovation. Their scalability, speed, and compatibility with existing semiconductor processes position them as the dominant architecture for near-term and mid-term quantum applications. Demand from AI, biopharma, finance, and research continues to intensify, creating a strong foundation for investment value.
Companies such as SpinQ—offering superconducting hardware, chip design software, cloud services, measurement and control systems, and quantum programming tools—represent some of the most balanced and strategically advantageous investment opportunities in the sector. With strong technological depth and diverse application pathways, the superconducting quantum computing industry is poised to deliver sustained growth between 2025 and 2030.
For investors seeking exposure to deep technology with transformative long-term potential, superconducting quantum computing remains one of the most compelling opportunities of the coming decade.
Featured Content






